Quick Links
Key Takeaways
- Rebooting into safe mode on Windows 11 can help resolve issues with starting your PC and make it more stable. Access it by shift-clicking "Restart" in the Start Menu, then go to Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Startup Settings.
- Use the "msconfig" utility to quickly enter safe mode. Open Start Menu, search "msconfig," select "System Configuration," go to the "Boot" tab, tick the box next to "Safe Mode," and click "Apply" and restart your PC
- Another way to enter safe mode is through the Settings app. Open Settings, click "System" > "Recovery," locate "Advanced Startup," click "Restart Now," then select "Troubleshoot" > "Advanced Options" > "Startup Settings" > "Restart."
If you're having trouble starting your Windows 11 PC, it might help to reboot into safe mode, which temporarily disables drivers and features to make your PC more stable. Here's how to do it.
How to Enter Safe Mode at Boot
With Windows 7 and earlier, you could typically start Safe Mode by pressing a function key (such as F8) just after turning on your PC. Microsoft removed this feature starting in Windows 8 because, thanks to new technologies, startup times became too fast for someone to quickly hit F8 in time before Windows loaded.
Instead, Microsoft designed an "automatic failover" workaround for times when your PC malfunctions and Windows won't load properly. Your PC will automatically enter an advanced startup troubleshooting mode if it fails to start twice in a row. You can force this by powering on the PC, and then pushing its physical power button just as you see the manufacturer's logo appear. Do this twice, and you'll see a "Choose an Option" advanced startup screen. Then, follow the directions described in the section below to enter Safe Mode.
Enter Safe Mode with msconfig
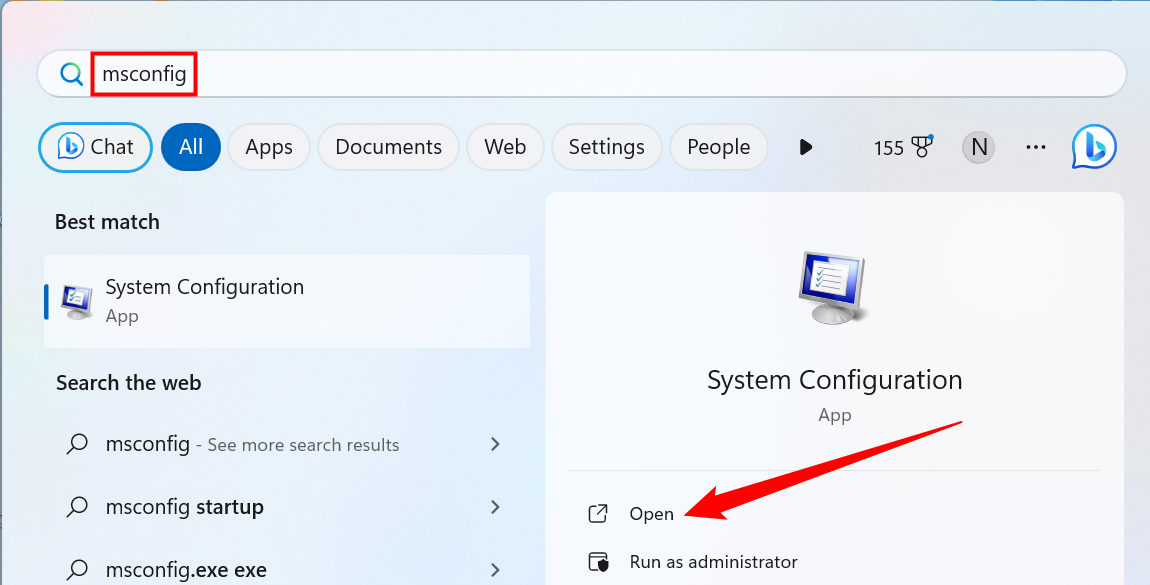
The quickest way to get into Safe Mode in Windows 11 is with the "msconfig" utility. Open up the Start Menu, search "msconfig," and select "System Configuration."
You may also open a Run window (Windows + R) and enter "msconfig" there instead.
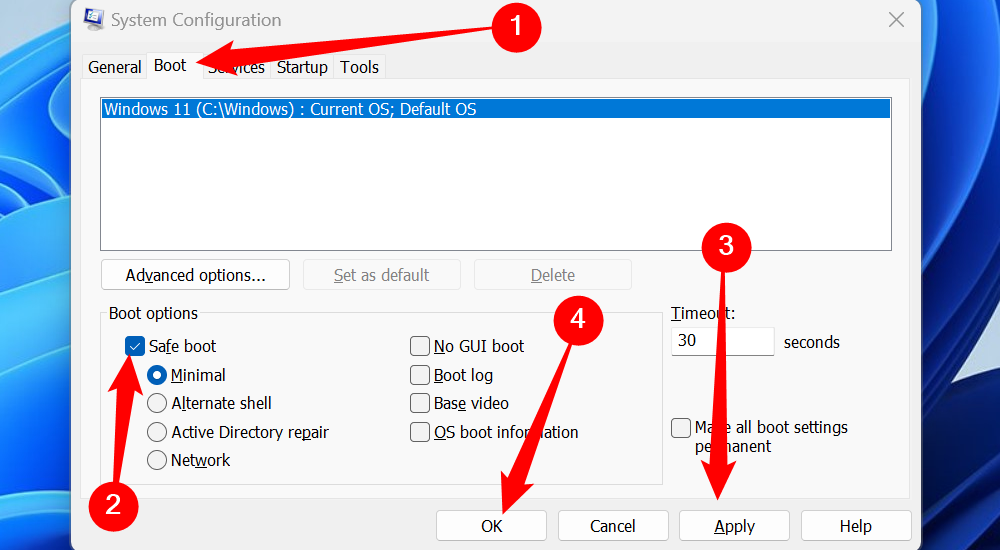
Head over to the "Boot" tab, tick the box next to "Safe Mode," and then click "Apply" and "OK." If you want to boot into Safe Mode with Networking, make sure you click the bubble next to "Network" under "Boot Options."
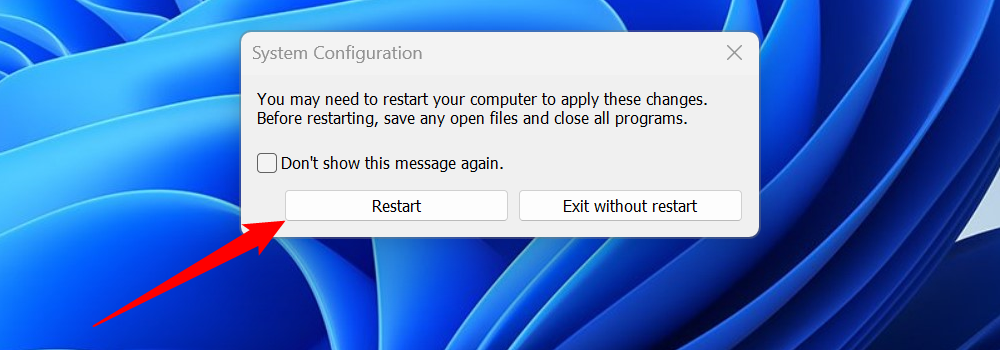
Once you click "OK" you'll get a second popup that allows you to restart immediately. Even if you opt to "Exit without restart," the next time you restart your PC it will boot into Safe Mode.
How to Enter Safe Mode from Windows
The process to enter Safe Mode on Windows 10 is very similar, but the interface looks a little different.
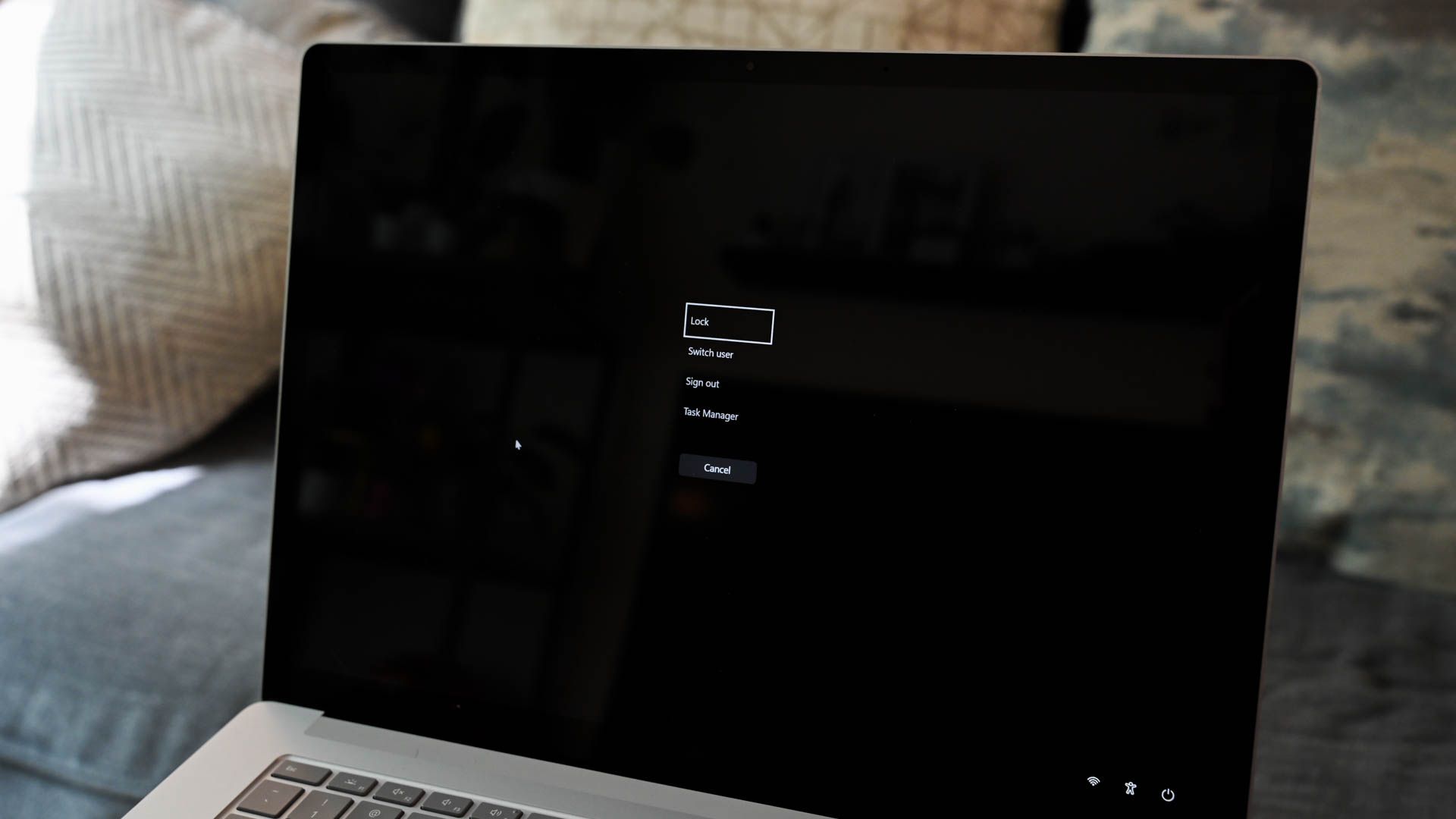
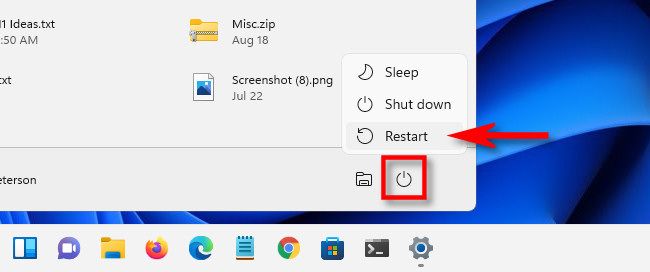
There are several different ways to restart your computer into an "Advanced Startup" mode on Windows 11 that will allow you to select "Safe Mode" after several choices. The easiest way? Open the Start menu and click the power icon in the lower-right corner. Then, hold down the Shift key on your keyboard and click "Restart."
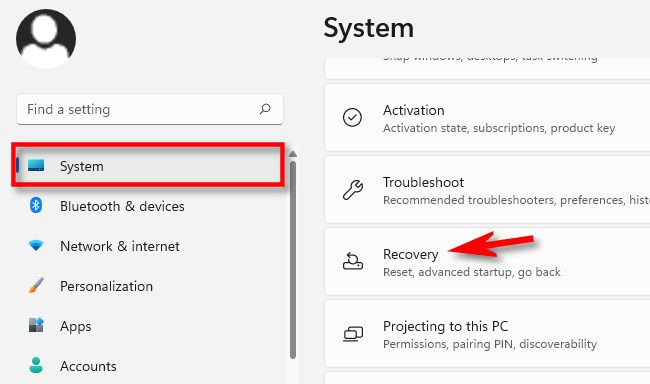
Alternately, you can begin the long road to Safe Mode through the Settings app. First, launch Settings by pressing Windows+i (Or, you can find it by searching in Start.). When Settings opens, click "System" in the sidebar, and then select "Recovery."
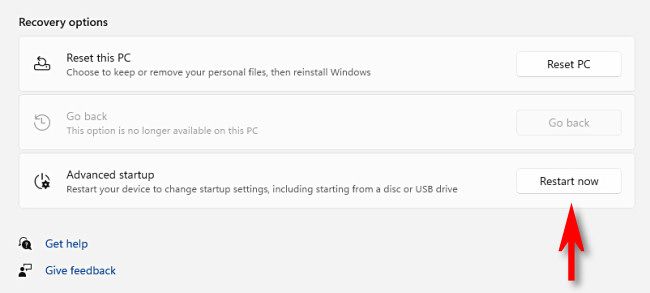
In Recovery Options, locate the "Advanced Startup" option and click the "Restart Now" button beside it.
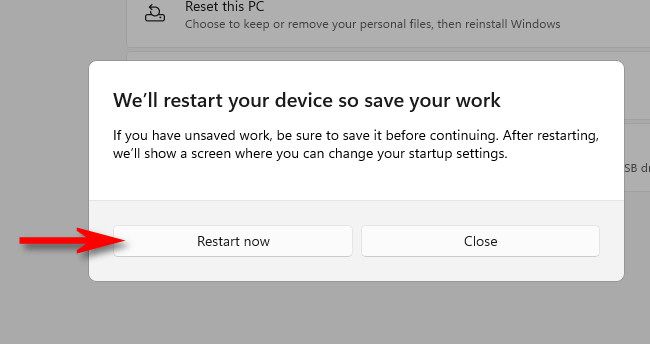
Windows will confirm with a pop-up dialog box that asks you to save your work before you restart. When you're ready, click "Restart Now."
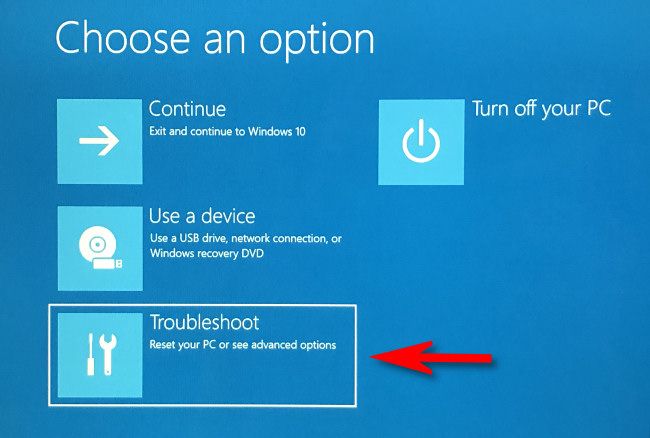
After that, Windows will shut down and restart into a blue-colored screen titled "Choose an Option," with several options in a brief list. Select "Troubleshoot."
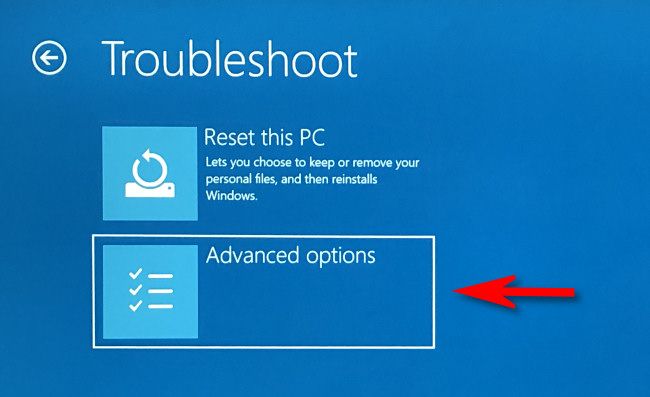
In Troubleshoot, select "Advanced Options."
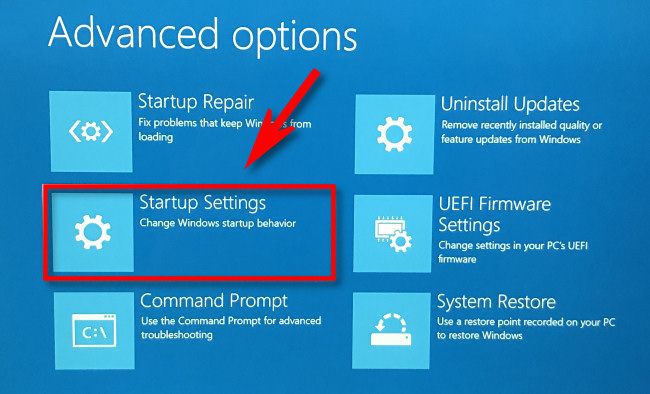
In Advanced Options, select "Startup Settings."
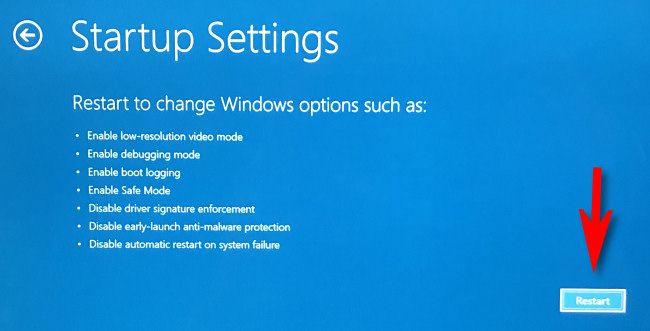
In Startup Settings, click "Restart."
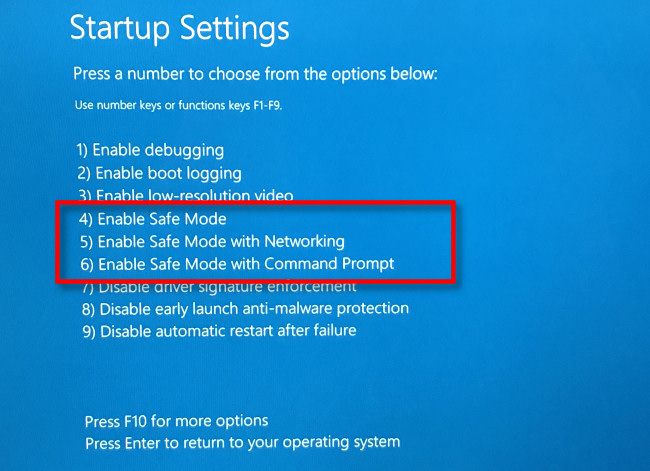
The PC will restart into a "Startup Settings" menu with nine numbered options. Press the "4" key on your keyboard for Safe Mode, "5" for Safe Mode with Networking, or "6" for Safe Mode with Command Prompt.
Generally, you'll want to press 4 or 5 here, but 6 can be useful for advanced troubleshooting if you're good with the Windows command line.
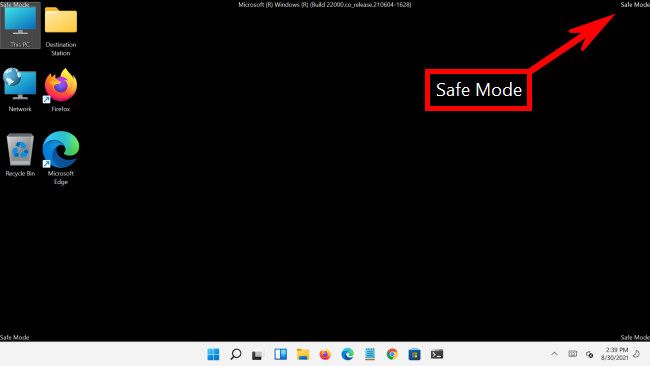
Once you've made your selection, Windows will finally boot into Safe mode. Your display will be at a lower resolution, and Windows will replace your desktop image with a black background that says "Safe Mode" in the corners.
At this point, you can do whatever troubleshooting tasks you need to accomplish. When you're done, just restart (or shut down) your Windows 11 PC as usual. If all goes well and your problem has been fixed, when you reboot the next time, you will exit Safe Mode and be back in regular non-safe Windows mode. Good luck!