Quick Links
Most operating systems have a built-in task manager or resource monitor that lets you see all active processes and programs running on your computer. The Chrome web browser also has one that helps you end troublesome tabs and extensions.
Open Chrome's Task Manager
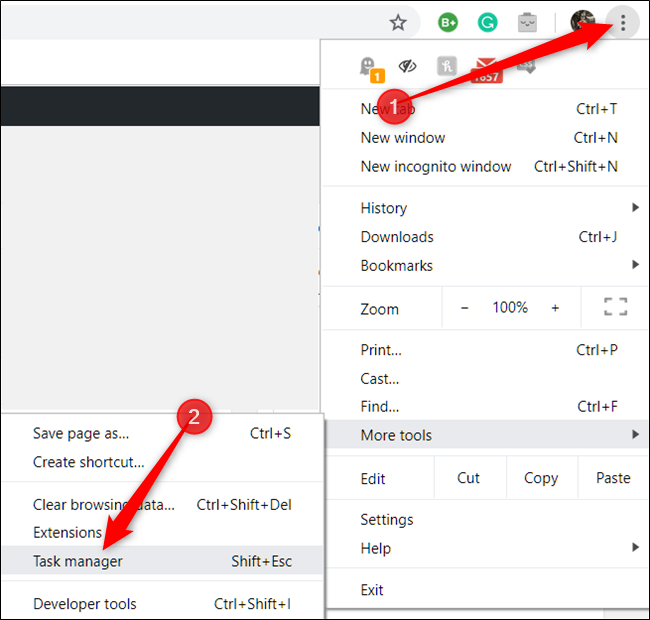
To open Chrome's Task Manager, click the "More" button (three dots), hover over "More Tools," and then click on "Task Manager." Alternatively, press Shift+Esc on Windows or Search+Esc on Chrome OS to open Task Manager.
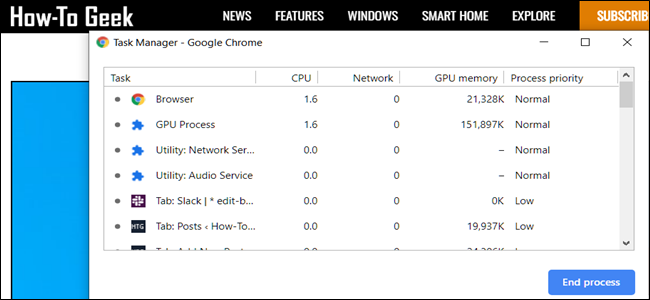
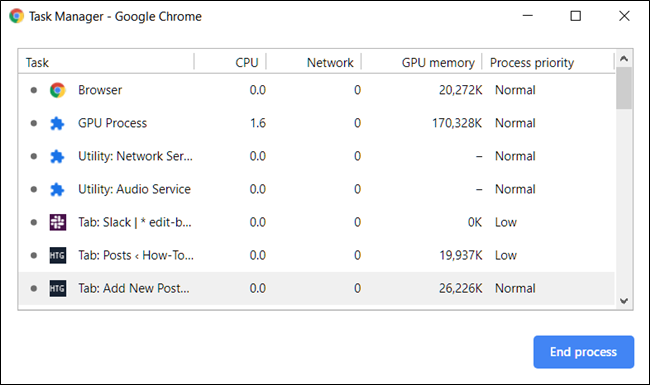
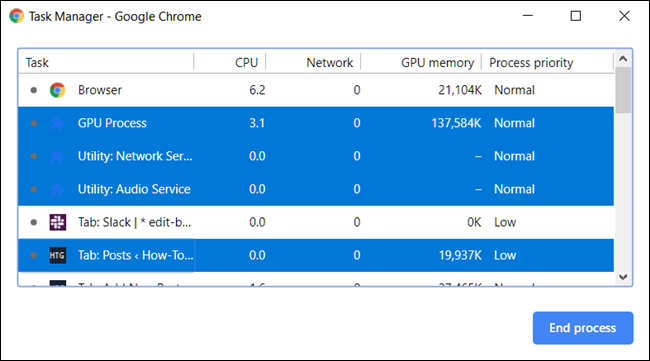
With Chrome's Task Manager now open, you can see a list of all tabs, extensions, and processes currently running in the browser.
End Troublesome Processes
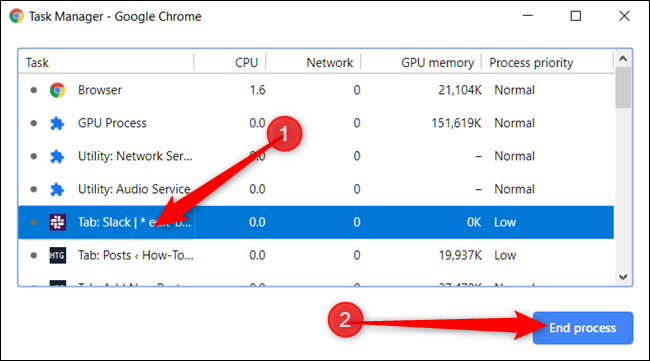
You can end any of the processes from this menu, which can be helpful when an extension or tab stops responding. To do this, click on the process and then select "End Process."
You can kill more than one process at a time by holding down the Shift or Ctrl key (Command on Mac), highlighting multiple items from the list, and then hitting the "End Process" button.
View Which Resources Tasks Are Using
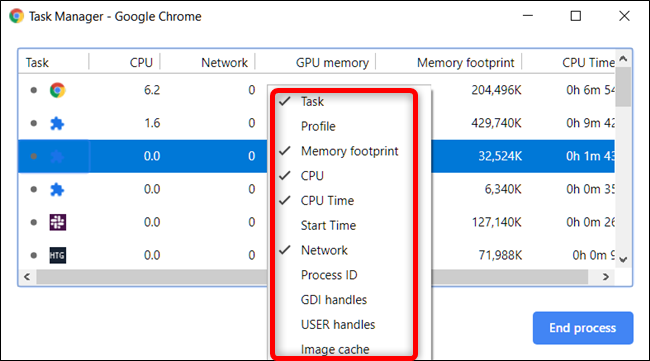
However, if you're here to use Task Manager to see which resources each task is using up, Chrome has over 20 categories of stats you can add as new columns. Right-click a task and a context menu will appear with a full list of available stats to choose from.
Click on any additional categories to add them to Task Manager. Categories that have a checkmark next to them are already displayed. If you want to remove a specific stat, click on the category and ensure the checkmark is removed.
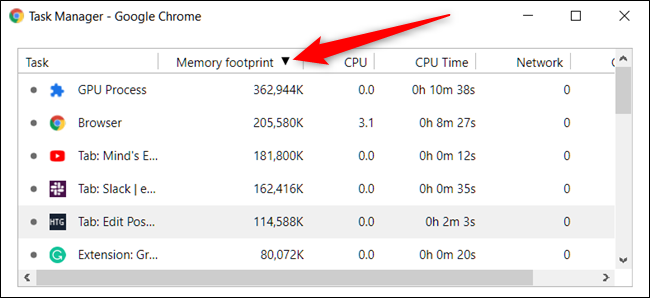
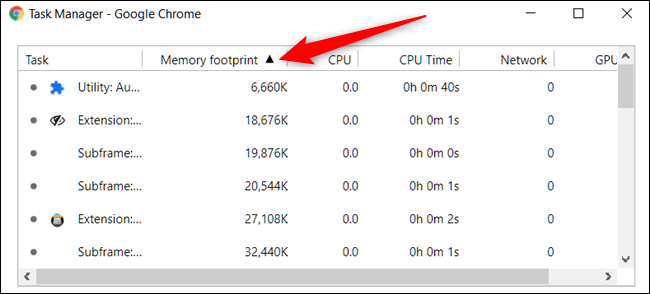
You can sort specific columns by clicking on a heading. For example, when you click on the Memory Footprint column, the process hogging up the most memory will be sorted to the top of the list.
Click on it again to put the process using up the least amount of memory at the top of the list.
Pro Tip: When you double-click on a tab, extension, or subframe in Task Manager, Chrome will send you directly to the tab. If you clicked on an extension, Chrome sends you to the settings page for that extension in
chrome://extensions
.