If your PC has been feeling buggy or having trouble during startup, it's possible that Windows system files have become corrupt, gone missing, or even have been changed by a software installation somewhere along the line. Like most versions of Windows before it, Windows 10 includes a Command Prompt utility named Windows Resource Protection that will scan, verify, and fix system files.
If your system is able to start, even in Safe Mode, you can run the utility right from Windows. If Windows won't start, you can also run it from the Command Prompt available when you boot from your installation media into repair mode.
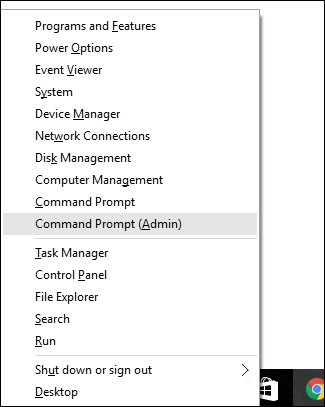
To run this utility in Windows, you will need to open the Command Prompt in administrator mode. Right-click on the Start menu or press Windows+X on your keyboard, and choose "Command Prompt (Admin)" from the Administrative Tools menu. You can also just use this nifty keyboard shortcut.
When you have the Command Prompt open in administrator mode, you can run the utility by using the following syntax:
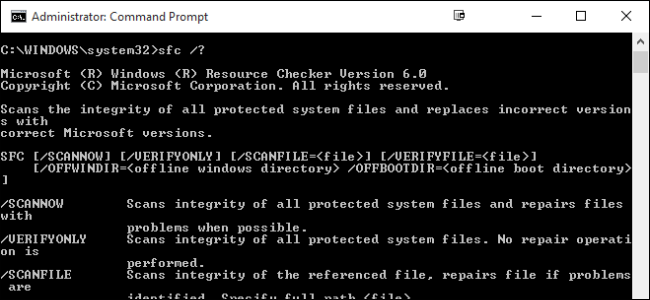
SFC [/SCANNOW] [/VERIFYONLY] [/SCANFILE=<file>] [/VERIFYFILE=<file>]
[/OFFWINDIR=<offline windows directory> /OFFBOOTDIR=<offline boot directory>]
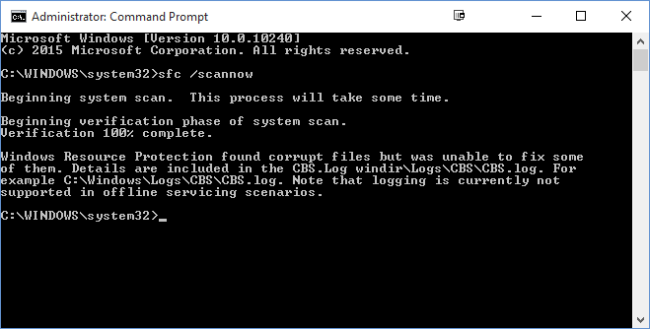
The most useful option is just to scan the whole system immediately, which will scan and attempt to repair any files that are changed or corrupted. You can do that with this command:
sfc /scannow
Alternatively, you can use the command sfc /verifyonly to scan for problems, but not perform any repairs.
You can also just scan or verify a particular file using the /scanfile=<file> or /verifyfile=<file> options along with the full path of the target file, like this:
sfc /scanfile=c:\windows\system32\kernel32.dll
As we mentioned, this utility does exist for previous versions of Windows, but you may encounter slightly different options. You can always use the command sfc /? to get all supported options for your version of Windows. And just in case you're wondering why Windows Resource Protection uses the command SFC, it's because the utility used to be named System File Checker.